Safe Sex
About 85% of sexually active women who do not use contraceptives become pregnant within a year. A woman can also become pregnant while breastfeeding and from about 10 days after childbirth and even during her menstruation. Withdrawal of the penis prior to ejaculation during intercourse (coitus interruptus) and periodic abstinence do not effectively prevent pregnancy nor provide protection against STDs. Here you can read more about several forms of contraceptives.
You can prevent an unwanted pregnancy with:
1- Total Abstinence
2- Use of contraceptives
To prevent unwanted pregnancy always use a form of contraception when you are sexually active.
Contraception methods
No method of contraception gives a 100% protection.
The male latex condom is the only contraceptive method considered highly effective in reducing the risk of STDs. Birth control pills, Implant and IUDs do not protect against STD infection.
For the Woman
DIAPHRAGM is a rubber disk with a flexible rim that covers the cervix and must be used together with spermicide. The diaphragm protects for six hours and should be left in place for at least six hours after the last intercourse but not for longer than a total of 24 hours.
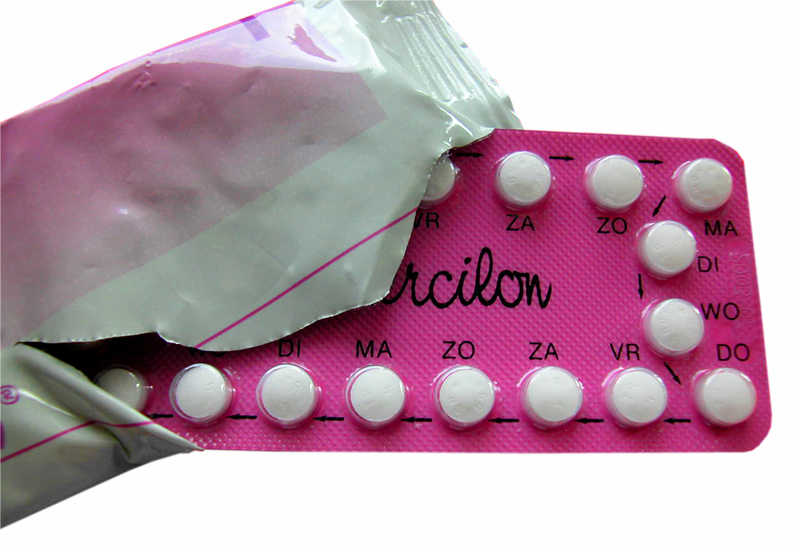
ORAL CONTRACEPTIVES protect against pregnancy by the combined actions of the hormones estrogens and progestin. The hormones prevent ovulation. The pills have to be taken every day as directed and do not work after vomiting or diarrhoea. Side effects of the pill can be nausea, headache, breast tenderness, weight gain, irregular bleeding, and depression.
Contraceptive patch. consists of a patch containing the hormones estrogen and progestogen. The patch should be changed every week. Side effects may include nausea, headache, breast tenderness, weight gain, irregular bleeding and depression.
Contraceptive ring consists of a ring containing the hormones estrogen and progestin, which you insert into the vagina. You wear the ring for 3 weeks. After that, the ring must be replaced. Side effects can include nausea, headache, breast tenderness, weight gain, irregular bleeding and depression.
DEPO-PROVERA is a hormonal contraceptive injected into a muscle on the arm or buttock every three months. The injection must be repeated every 3 months. The menstruation can become irregular and sometimes even absent.
IMPLANTS (such as Norplant or implanon) are made up of small rubber rods, which are surgically implanted under the skin of the upper arm, where they release the contraceptive steroid levonorgestrel. Their protection lasts from 3 to 5 years. Side effects include menstrual cycle changes, weight gain, breast tenderness and loss of bone mass.
IUD is a T-shaped device inserted into the uterus by a health-care professional. The IUD can remain in place for 5- 10 years. IUD’s have one of the lowest failure rates of contraceptive method. Sometimes the IUD can be expelled and a woman has to check each month after her period with her finger if she can still feel the threads of the IUD. Other side effects can include abnormal bleeding, and cramps but this occurs mostly only during and immediately after insertion.
Hormonal-IUD is an IUD with a small hormonal (progestogen) sleeve. It is one of the most effective forms of birth control. Next, to the above-mentioned characteristics of an IUD, it can remain in place for 5 years but has no heavy bleeding side effects. As most women experience only lighter periods and less bleeding (some stop completely having periods), it’s supposed to be a perfect therapy as well for women with heavy cycle bleedings.
FEMALE STERILIZATION is done surgically. The tubes are ligated as a result of which the egg-cells can not encounter the sperm cells anymore and thus the woman can not get pregnant. It is a permanent form of contraception.
FEMALE CONDOM is made of soft rubber and can be used only once. As a mechanical barrier method of contraception worn by women it’s inserted easily into the vagina before sex and prevents direct vaginal contact with semen, infectious genital discharges, and genital lesions It is shaped like a long tube or sheath, with one closed end and one open end, and at each end, there's a flexible ring, helping to keep the female condom in place once it's inserted. Condoms are the most effective method for reducing the risk of infection from the viruses that cause AIDS and other sexually transmitted diseases (STD’s).
EMERGENCY CONTRACEPTION should be used after unprotected sex to prevent unwanted pregnancy. There are 2 types of morning after pills. You must take the morning after pill with levonorgestrel within 72 hours (3 days) and the morning after pill with ulipristal or mifepristone within 120 hours (5 days). More information can be found at the Emergency Contraception website http://ec.princeton.edu/ This website will also inform on the what type of EC and birth control pills are available in your country and how to use them as emergency contraceptives.
MORNING-AFTER IUD must be inserted within 5 days of unprotected intercourse. The IUD can stay for 5 to 10 years.
For the Man
CONDOMS are mostly made from latex rubber and can be used only once. Some have spermicide added to kill sperm. They act as a mechanical barrier, preventing direct vaginal contact with semen, infectious genital discharges, and genital lesions. Condoms are the most effective method for reducing the risk of infection from the viruses that cause AIDS and other sexually transmitted diseases (STD’s). It is important to use it well and put the condom on before intercourse
MALE STERILIZATION also known as vasectomy, is a quick operation performed under local anaesthesia with possible minor post-surgical complications, such as bleeding or infection. The ability to get an erection and an ejaculation does not disappear. The sperm cells are just a very small part (1%) of the fluid and a man will not notice any difference in ejaculation. The body will absorb the sperm cells.
Safety rates of different methods of contraception
Estimated Effectiveness:
• Male Latex Condom 86%.
• Female Condom 79%.
• Diaphragm with Spermicide 80%.
• Oral Contraceptives Over 95%.
• Injection (Depo-Provera) Over 99%.
• Implant (Norplant, Implanon) Over 99%.
• IUD (Intrauterine Device). 98-99 %
• Surgical Sterilisation Over 99%
• Emergency Contraceptives: 75%.
Lowest expected Typical Use Pregnancy-rate Pregnancy-rate
• Male Sterilisation 0.15% 0,1%
• Female Sterilisation 0.5% 0,5%
• Implant 0.09% 0,9%
• Hormone Shot 0.3% 0,3%
• Combined Pill 5% 0,1%
• Minipill (Progestin only) 5% 0,5%
• IUD 0.8% 0,6%
• Condom 14% 3%
• Diaphragm 20% 9%
• Periodic abstinence 5-40%
• No Method: 85% 85%
What is an STI or Sexual Transmitted Infection?
You can get an STI by sexual intercourse but also through oral sex, anal sex or…
Services offered by Women on Waves
Information about and provision of contraceptives
Information about and…